Nesting is a crucial technique in research that allows you to capture the various expressions and nuances associated with your topic. Often, concepts can be described in multiple ways, and nesting helps ensure that all relevant terms are included in your search.
Using parentheses ( ) to group similar terms together, nesting instructs the database to prioritize searching for terms within the parentheses before considering the rest of the search query. Additionally, nesting utilizes Boolean operators like OR and AND to connect related terms and refine the search results.
For instance, consider the topic of mental health among young individuals. To encompass the various terms used to describe this demographic, such as teenagers, adolescents, or young adults, you might construct a nested search like this:
(teenager OR teen OR adolescent OR youth OR “young adult”) AND depression
This search ensures that the database retrieves articles containing any of the terms within the parentheses, along with the term “depression.”
Furthermore, nesting is valuable when exploring different aspects of a topic simultaneously. For instance, if you’re interested in understanding both the symptoms and treatments of schizophrenia, you could employ the following nested search:
(symptoms OR treatments) AND schizophrenia
By nesting the terms related to symptoms and treatments within parentheses and connecting them with the Boolean operator AND, you focus your search on articles discussing both aspects of schizophrenia.
The importance of nesting becomes evident when comparing search results with and without proper nesting. Omitting parentheses can significantly alter the scope and relevance of search results, leading to potentially irrelevant findings.
For example, consider the search queries:
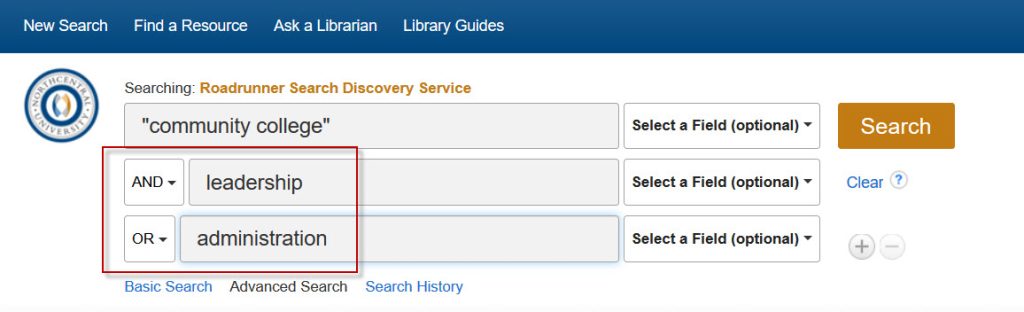
“community college” AND (leadership OR administration)
“community college” AND leadership OR administration
In the first query, proper nesting ensures that the terms “leadership” and “administration” are connected to “community college.” However, in the second query, the absence of parentheses disconnects “administration” from the rest of the search, resulting in a broader and potentially less relevant set of results.
In databases like Roadrunner and EBSCOhost, which offer drop-down menus for Boolean operators, it’s crucial to exercise caution and ensure proper nesting to avoid unintentional search errors. Always verify that your search query accurately reflects your intended nesting structure to retrieve the most relevant information.
Instead, it’s advisable to employ the nesting technique within a single search box, as demonstrated below.
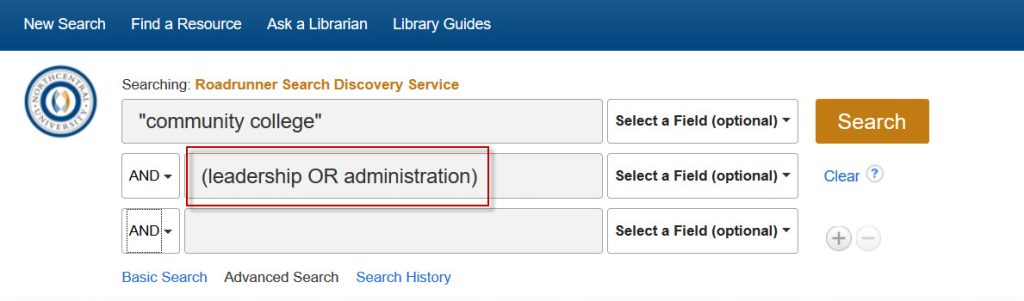
As demonstrated in the example above, we are employing nesting alongside the phrase searching technique. It’s worth noting that nesting can be combined with other advanced search techniques to create more intricate searches, similar to the one illustrated below:
scssCopy code
(alcohol OR drug OR (substance N3 abuse)) AND (teenagers OR adolescents)
However, it’s important to acknowledge that there may be certain Library databases where nesting is not supported. We suggest clicking on the database help link (usually located in the upper right corner) to ascertain if nesting is permitted. Additionally, feel free to reach out to the Library if you have any inquiries.
