Proximity searching is a valuable tool that allows you to refine your search by specifying how closely two or more search terms appear in the search results. This feature becomes particularly useful when you are exploring concepts expressed by various phrases or when you want to capture nuanced variations of a topic.
For instance, suppose you’re interested in exploring “curriculum theories.” A regular phrase search for this term might overlook documents discussing “theories of curriculum,” “theories involving curriculum,” or “theories about curriculum.” However, by employing proximity searching, you can instruct the database to retrieve results where the term “curriculum” appears within a specified number of words from the term “theories.”
Proximity searches typically employ operators that indicate the proximity and order of the search terms. These operators consist of a letter (N or W) or word (NEAR) followed by a number indicating the maximum number of words allowed between the search terms. The maximum number of words varies across databases, typically ranging from 10 to 255. It’s important to note that a lower number results in a narrower search.
For example:
- “curriculum N3 theories” searches for “curriculum” within 3 words of “theories,” irrespective of order.
- “curriculum W3 theories” searches for “curriculum” within 3 words of “theories,” in the exact order specified.
It’s crucial to be aware that different databases may use different proximity operators. Consult the database’s help menu to determine the symbols it employs. Below are examples of proximity searches in popular NU Databases, as well as Google.
Instructions
EBSCOhost & Roadrunner search
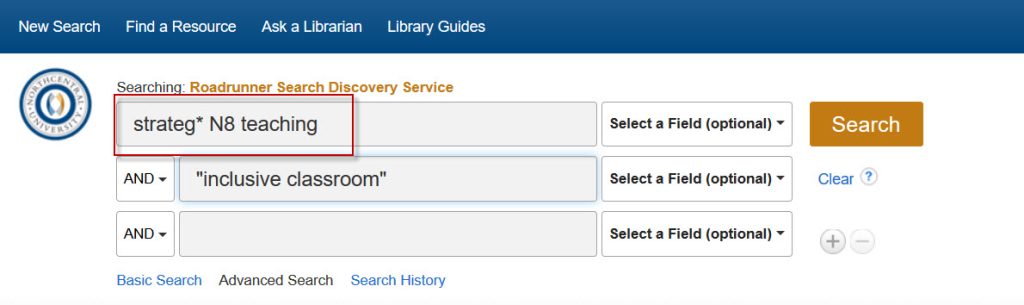
The Near Operator (N) allows you to specify how closely two search terms should appear in relation to each other within the search results. For instance, N5 indicates that the words can be a maximum of five words apart, regardless of their order in the text.
For example, in Roadrunner, a search for “strategy N8 teaching N8 inclusive classroom” would retrieve results containing the terms “strategy” or “strategies” within eight words of “teaching” (in any order) and also the exact phrase “inclusive classroom.”
On the other hand, the Within Operator (W) narrows down the search by requiring the terms to appear within a specific number of words from each other and in the exact order specified.
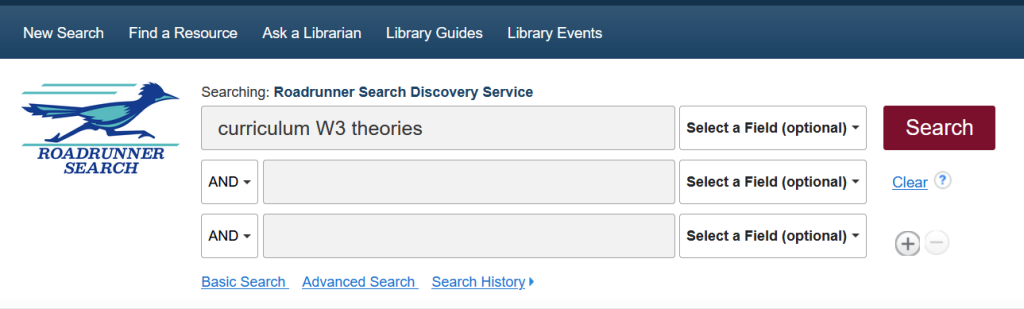
For instance, a search for “curriculum W3 theories” would look for the term “curriculum” within three words of “theories,” in the exact order entered. This means that it will retrieve articles discussing “curriculum theories,” “curriculum design theories,” or “curriculum reform theories,” but not “theories of curriculum design” or “theories of curriculum reform.”
These operators are particularly useful for refining searches and obtaining more relevant results.
NavigatorSearch is a powerful tool that allows users to search across all subscribed EBSCO databases simultaneously. It provides access to a wide range of scholarly journals, e-books, videos, and other resources from various disciplines. However, it’s important to note that not all library databases and publisher content are searchable through NavigatorSearch, and some databases may need to be searched individually for specific information due to unique content offerings. NavigatorSearch can be accessed at https://resources.nu.edu.
Gale Academic OneFile
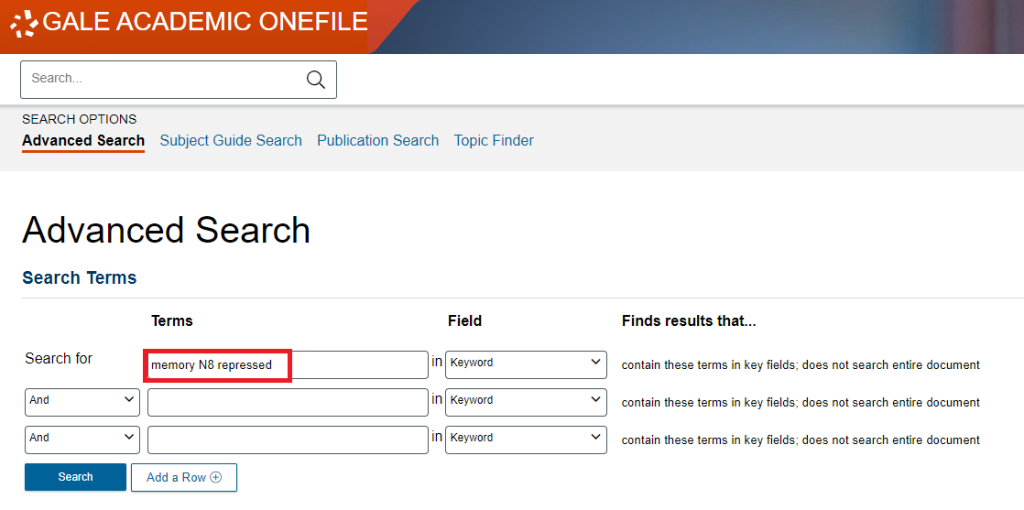
The Near Operator (N) is a powerful tool in database searching, allowing users to specify the proximity of two search terms within the search results. With N5, for example, the operator finds words that are a maximum of five words apart, regardless of their order in the text.
For instance, in Gale Academic OneFile, a search for “memory N8 repressed” would retrieve results containing the term “memory” within eight words of “repressed,” in any order.
Gale Academic OneFile offers a wide array of multidisciplinary content, encompassing various formats such as academic articles and magazines. Its primary purpose is to provide users with a comprehensive range of content covering diverse topics across different source types.
The platform boasts several special features to enhance user experience, including a visualization tool and a browse-by-topic feature, facilitating topic brainstorming. Additionally, it includes a Lexile feature for filtering texts by difficulty, enabling users to find content suitable for their reading level. Moreover, users can highlight and add notes to text, enhancing the research process. Furthermore, the read-aloud feature promotes accessibility by allowing users to listen to the content.
Navigator Search serves as a gateway to Gale Academic OneFile and other resources, enabling users to search across multiple databases simultaneously. This integrated approach ensures users have access to a wealth of information to support their research endeavors.
ProQuest
The Near Operator (N/ or NEAR/) is a powerful tool for refining database searches, enabling users to specify the proximity of search terms within the search results. With N/5 or NEAR/5, for instance, the operator finds words that are a maximum of five words apart, regardless of their order in the text.
For example, in ProQuest Central, a search for “strategy NEAR/8 teaching” would retrieve results containing the term “strategy” or “strategies” within eight words of the term “teaching,” in any order, and also include the exact phrase “inclusive classroom.”
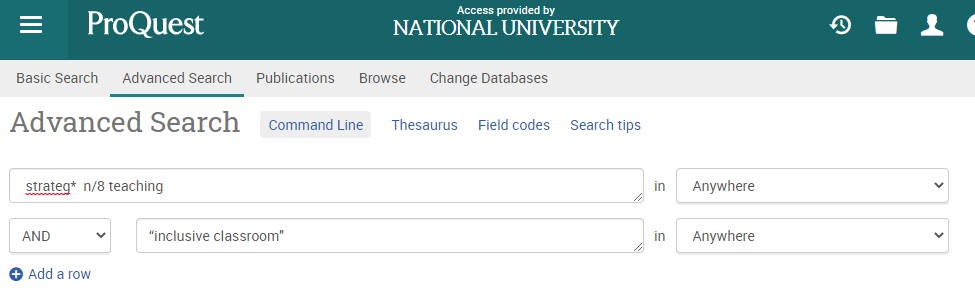
This functionality enhances precision in searches, allowing users to pinpoint relevant content even when the terms are not adjacent. It is particularly useful when exploring concepts that may be expressed using different phrases or when seeking information within a specific context.
By utilizing the Near Operator, researchers can efficiently navigate databases and retrieve targeted results that align closely with their information needs.
ProQuest Central is a comprehensive collection comprising more than 30 subject-specific databases covering a wide range of disciplines, including Business, Health and Medical, Social Sciences, Education, Science and Technology, and Humanities. This vast repository allows students to access a wealth of peer-reviewed research across various fields, providing valuable insights and information.
In addition to its extensive content, ProQuest Central offers special features such as a Thesaurus tool, which assists users in navigating the database’s controlled vocabulary, and a read-aloud feature, enhancing accessibility and usability for researchers.
PQDT
The Near Operator (N/ or NEAR/) is a valuable tool for refining database searches, allowing users to specify the proximity of search terms within the search results. With N/5 or NEAR/5, for instance, the operator finds words that are a maximum of five words apart, regardless of their order in the text.
For example, in ProQuest Dissertations & Theses, a search for “teacher NEAR/5 perception AND “inclusive classroom” AND elementary” would retrieve results containing the term “teacher” within five words of the term “perception,” in any order, as well as the exact phrase “inclusive classroom” in the abstract of the article. Additionally, the search would include the word “elementary” anywhere in the content.
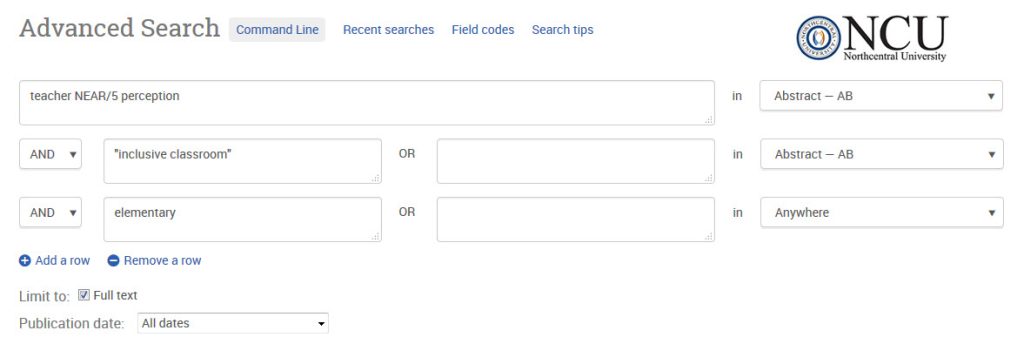
This functionality enhances precision in searches, allowing researchers to pinpoint relevant content even when the terms are not adjacent. It is particularly useful when exploring concepts that may be expressed using different phrases or when seeking information within a specific context.
The ProQuest Dissertations & Theses database (PQDT) is the world’s most comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses. It serves as the database of record for graduate research, encompassing over 2.3 million dissertations and theses from around the world.
This extensive repository of scholarly works provides researchers with access to valuable resources for foundational research, locating test instruments, and accessing data. Additionally, PQDT offers special features such as the ability to search by advisor (chair), degree, degree level, or department, making it a versatile tool for academic inquiry. Furthermore, it includes a read-aloud feature, enhancing accessibility and usability for researchers.
ScienceDirect
The “Within Operator (W/)” is a search technique used to find words or phrases within a specific proximity to each other in a document. When employing this operator, such as W/5, it identifies words or phrases that are a maximum of five words apart from one another, regardless of their order of appearance.
For instance, executing a search in ScienceDirect with the operator W/4 would yield results containing the term “school” within a maximum of four words of the term “readiness,” and also include the exact phrase “teacher perception” within the document.
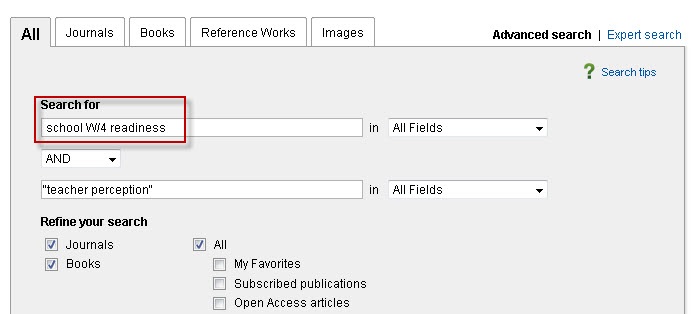
ScienceDirect is a comprehensive database provided by Elsevier, encompassing various fields including computer science, health science, and social sciences. It offers access to a plethora of peer-reviewed journal articles and book chapters, catering to both foundational and cutting-edge research.
Some key attributes of ScienceDirect include:
- Content: The database encompasses a wide array of topics ranging from theoretical discussions to practical applications across physical, life, health, and social sciences.
- Purpose: It serves as an invaluable resource for researchers seeking comprehensive coverage of scientific literature, facilitating exploration from foundational knowledge to the latest advancements.
- Special Features: ScienceDirect provides access to peer-reviewed articles and open-access content, ensuring a diverse range of scholarly material for users to explore and utilize in their research endeavors.
By utilizing the “Within Operator (W/)” in conjunction with databases like ScienceDirect, researchers can refine their searches to pinpoint relevant information more effectively, thereby enhancing the efficiency and precision of their research process.
Web of Knowledge
The “Near Operator (NEAR/)” is a search tool utilized to identify words or phrases within close proximity to each other in a document. When employing this operator, such as NEAR/5, it retrieves words or phrases that are a maximum of five words apart from one another, irrespective of their order of appearance.
For instance, conducting a search in Web of Knowledge with the NEAR/7 operator would yield results containing the term “information” within a maximum of seven words of the term “security,” and also include either the term “hospital” or the exact phrase “medical center” within the document.
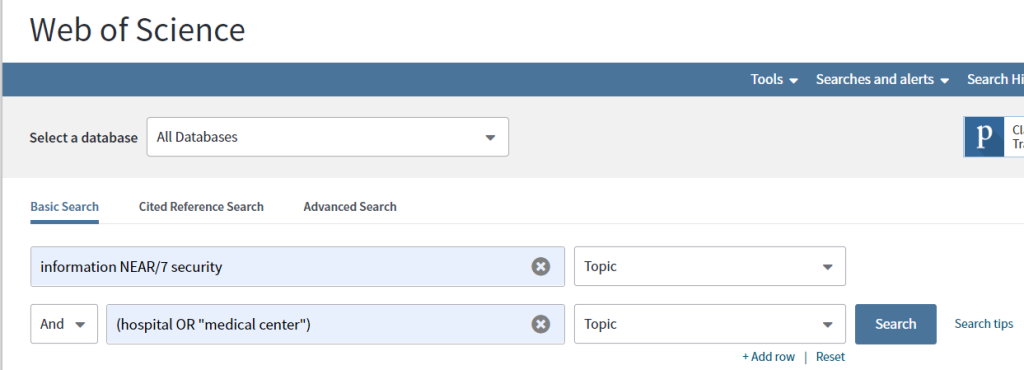
Web of Science is a comprehensive platform providing access to citations and articles across multiple disciplines. It serves as a valuable resource for conducting topic searches and identifying additional resources that have cited a specific reference, facilitating the exploration of citation networks.
Key features of Web of Science include:
- Content: The database encompasses citations and articles from various fields not accessible through NavigatorSearch, offering a diverse range of scholarly material.
- Purpose: It is utilized for conducting comprehensive topic searches and navigating citation networks to discover additional resources related to specific references.
By utilizing the “Near Operator (NEAR/)” in conjunction with databases like Web of Science, researchers can refine their searches to pinpoint relevant information more effectively. This enhances the efficiency and precision of their research endeavors, allowing for in-depth exploration of topics across different disciplines.
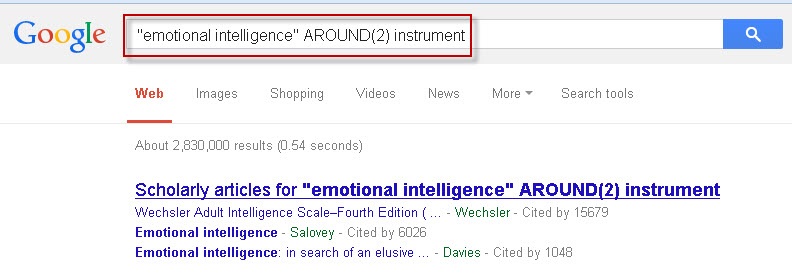
The “AROUND()” operator is a powerful tool used in search engines to identify words or phrases within close proximity to each other in a document. When employing this operator, such as AROUND(5), it retrieves words or phrases that are a maximum of five words apart from one another, regardless of their order of appearance.
For instance, conducting a search in Google with the AROUND(2) operator would yield results containing the exact phrase “emotional intelligence” within two words of the term “instrument,” in any order.
Google is a widely used search engine that offers a plethora of features to enhance research endeavors. By utilizing operators like AROUND(), researchers can refine their searches to pinpoint relevant information more effectively. This enhances the efficiency and precision of their research endeavors, allowing for in-depth exploration of topics across different disciplines.
Additional tips for using Google for research include:
- Utilize advanced search operators: Google offers various advanced search operators, such as site:, filetype:, and intitle:, to refine search results and locate specific types of content.
- Use quotation marks for exact phrases: Placing quotation marks around a phrase ensures that Google searches for the exact phrase rather than individual words scattered throughout the document.
- Exclude specific terms: By using the minus sign (-) before a term, researchers can exclude specific terms from their search results, refining the focus of their search.
- Explore Google Scholar: Google Scholar is a specialized search engine that indexes scholarly articles, theses, books, conference papers, and patents. It provides access to a vast repository of academic literature across various disciplines.
By incorporating these strategies and utilizing advanced search operators like AROUND(), researchers can leverage the full potential of Google for their research endeavors, accessing relevant and credible information with ease.